Professor and Chairman
Michelangelo Foti
Dept. of Cell Physiology and Metabolism - CMU - UNIGE Obesity, liver metabolic disorders and cancer
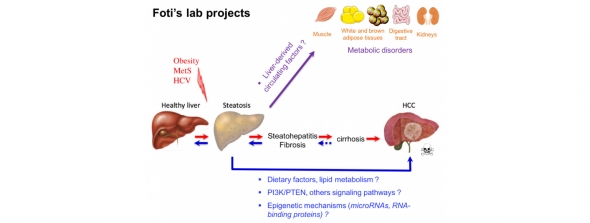
Obesity and the metabolic syndrome (MetS) are major etiological factors leading to hepatic metabolic disorders commonly referred as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). These include hepatic insulin resistance (IR) and steatosis, inflammation (steatohepatitis or NASH) and fibrosis development. Unfortunately, these metabolic disorders may then progress with time towards life-threatening diseases such as hepatic cirrhosis and cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC). In this regard, obesity and the MetS have reached pandemic proportions and incidences of NAFLD/NASH and HCC are expected to dramatically increase in the future.
Research in the Foti’s laboratory aims at understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the development of metabolic liver disorders associated with obesity and IR and their progression towards cancer. As well, the mechanisms by which the liver crosstalks with other peripheral organs (e.g. muscles, adipose tissues, gut and kidneys) to regulate homeostasis in physiopathological conditions are under investigation. In these different projects, our attention focuses in particular on the role of dietary fatty acids and hepatic PI3K/PTEN signalling in these processes, as well as on epigenetic mechanisms involving specific microRNAs and RNA-binding proteins.
In addition to common lab techniques and bio-imaging (MRI, CT-scan, optical and ultrastructural microscopy), state-of-the-art methodologies are applied to investigate hepatic/whole body metabolic disorders and liver cancer development using in vivo animal (mice under specific regimen or transgenic mice) and in vitro cell models (liver, muscle, adipose tissue, kidney, ..) , human samples and “omics” analyses.
Keywords
- Obesity
- Liver
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Insulin resistance
- Steatosis
- Steatohepatitis (NASH)
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
- Inter-organs communication
- Dietary fatty acids
- PI3K/PTEN signaling
- microRNAs
- RNA-binding proteins
Contact
Michelangelo FOTI
Professor and Chairman
Dept. of Cell Physiology and Metabolism
Faculty of Medicine, University of Geneva
Office C05.1531.a
1, rue Michel-Servet
CH-1211 Geneva, Switzerland
Tel.: +41 22 379 52 04
Fax: +41 22 379 52 60